EXL P&C Market Pulse
The US insurance industry – EXL Market Pulse
EXL does a Market Pulse every quarter of the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors that affect the insurance industry, highlighting the most urgent topic.
This six-factor framework helps the industry formulate the appropriate medium-to-long term strategy in response.
EXL Market pulse Q2 2022
- For Q2 2022, our analysis reveals that economic and technological factors are the most urgent. However, it is important to note that activity in every factor is high
- With a Q1 growth of -1.4% in the US economy, sharply down from +6.9% in Q4 2021, the economy is close to a formal recession. Negative sentiments, a slowing investment climate, and high inflation are all coming together to create a negative outlook for insurers
EXL Market Pulse for US P&C Insurance June 2022
Political
- Political unrest creates significant catastrophic events (CAT), costing US insurers approximately $2B in 2020 and Chilean insurers $3B in 2019.
- Stricter laws create financial impact: Privacy and data security laws cost insurers over $1T over the next 10 years. COVID-era laws like the CARES Act also increased costs.
- Political uncertainty: The Russia-Ukraine War has a $36B impact on the insurance industry. Increased cyber risks and uncertainty due to Brexit are additional complicating factors.
Economic (High Urgency)
- GDP growth sharply declined from 6.9% in Q4 21 to -1.4% in Q1 22
- 75% CEOs believe a recession will occur in 2023
- 6.2% higher core inflation reduces the economic value of insurers by approximately 8.4%, a trend exacerbated by increased claim severity, CAT events, and high claims costs
- Investment losses foreseeable as the Dow Jones declined by 13% YTD while the NASDAQ is down by 29%
Social
- Changing buying patterns for Millennials and Gen Z due to declining ownership rates and increased participation in the sharing economy
- Increasing importance of diversity, equity, and inclusivity
- Shifting consumer choices and needs due to hybrid working models, market competition, and insurtechs
Technological (Medium Urgency)
- 41% of consumers are likely to move to digital providers. 40% of InsurTechs are focused on marketing and distribution, placing an emphasis on customer experience (CX)
- 48% of insurance CIOs say their organizations do not have the tech capabilities for adapting to the changing market
- Tech costs for operations increased 36% for P&C between 2021 and 2020
- Data, digital, and new technologies are driving the need for quick pivots
Environmental
- There has been a $600B impact from natural disasters in the US over the last five years
- Rapidly changing riskiness of the entire insured pool
- 95% of insurers include climate change as factor in investments
- Pollution is impacting health and life expectancy
Legal
- Consumer privacy and data security laws are driving increased risk and compliance needs due to regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and autonomous driving laws
- Increased litigation against insurers due to securities class action litigations, cyber breaches, error and omissions, and defaulted M&A
- Employment and labor laws also raise the risk of litigation for organizations that operate in multiple countries due to changing regulations regarding remote work and other areas
Economic factors impacting insurers in the US in 2022
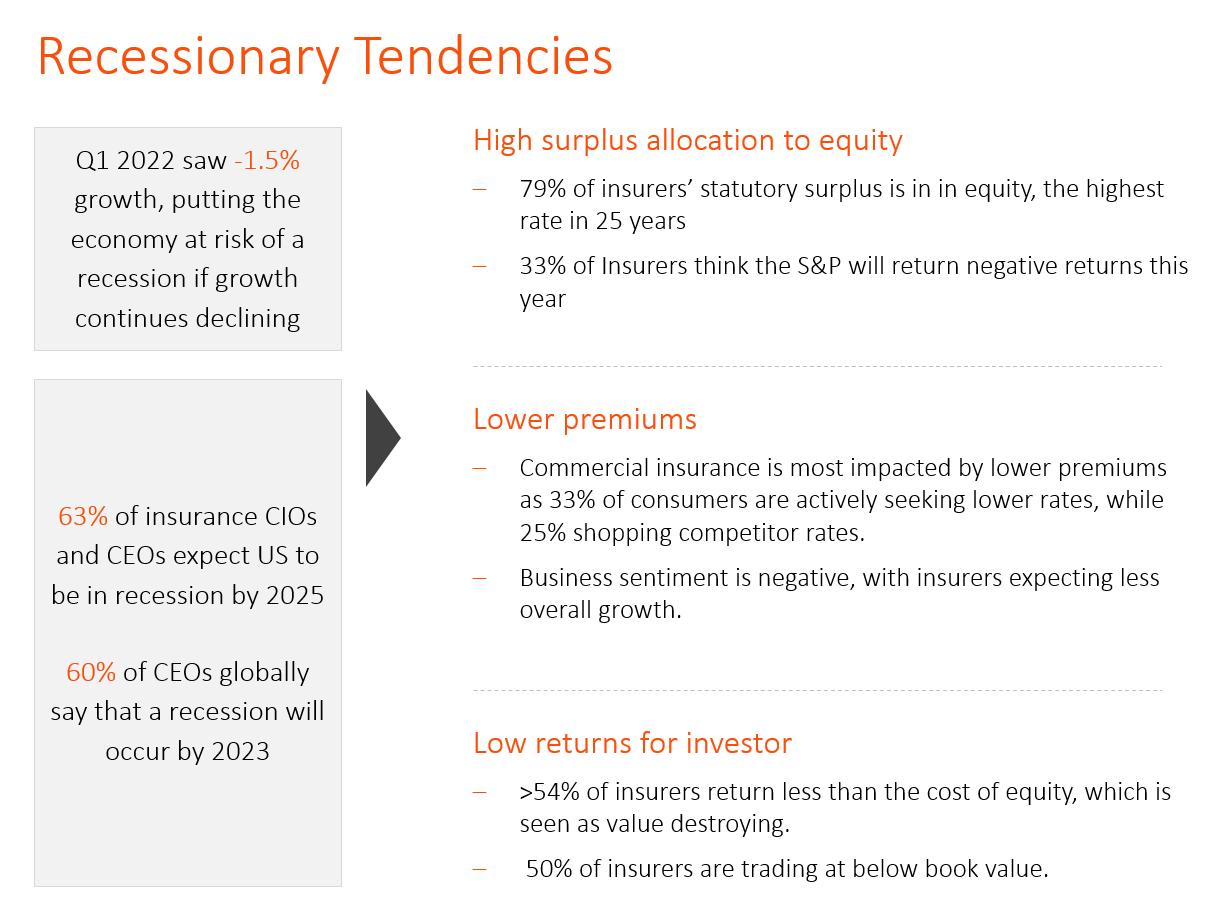
Insurance companies have traditionally thrived more on their investment income than their core underwriting business. Competitive pricing and below-par risk ratings have previously been protected by shrewd investment decisions. Given the outstanding returns, insurers have invested unprecedented amounts of their statutory surplus in equity over the past few years. With equity assets now at risk and premiums expected to decline, the industry faces major headwinds as even investors do not see the industry as generating strong returns.
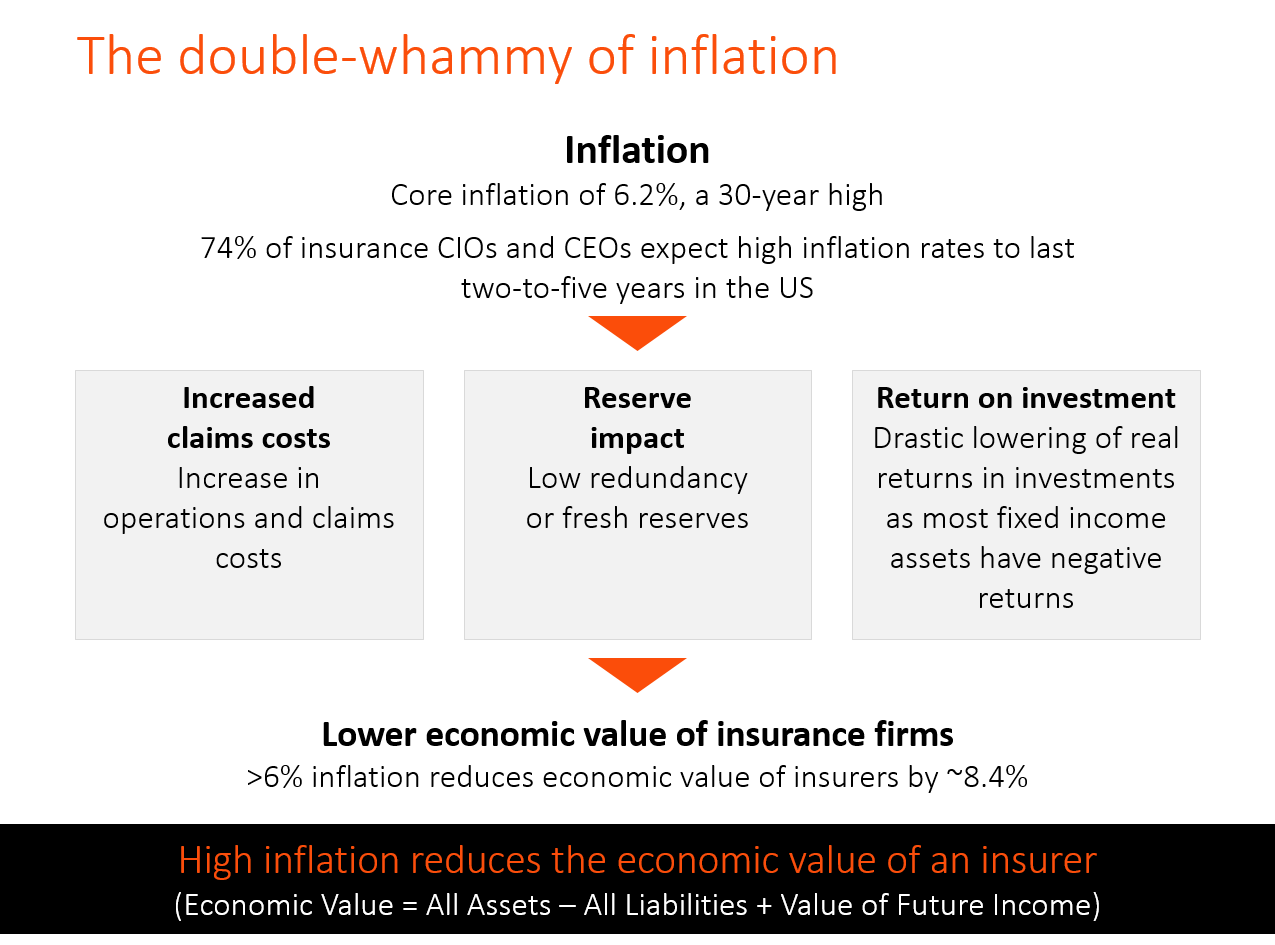
Higher inflation increases the cost of claims due to higher repair costs, medical bills, professional fees, and other expenses. Inflation also reduces the real rate of return for fixed income assets, pushing many organizations into riskier asset classes or raising more cash to meet claims obligations. Reserves calculated at lower core inflation rates are no longer adequate and are requiring fresh infusions. Higher costs necessitate higher premiums, which in turn makes individuals and businesses scale back on their insurance spend.
Detailed analysis of all other factors
Political factors impacting insurers in the US
- Political unrest, more stringent laws, and turbulent world politics make it a time of great risk for Insurers
- Instability and unrest is expensive
Political unrest creates significant CATs
- Political protest in 2020 cost US insurers about $2B. Global political unrest drives higher costs for insurers, with the 2019 protests in Chile costing $3B.
- For more than the last 70 years, the average yearly impact on insurance from these events has been $90M.
Privacy and data security laws
- More remote business and data access is driving higher cyber security incidents
- More stringent laws and higher penalties are creating the potential for costlier violations. Individual state laws alone could impose out-of-state costs of between $98B and $112B annually, over $1T over 10 years.
Cares Act and COVID-era laws
- More tax protections, such as a five-year carryback and 20-year carry-forward losses for non-life insurers
- Mandatory coverage of Covid testing, vaccinations and other measures affected expenses
Flood and earthquake benefit policies
- US is planning to revamp flood policies due to climate change.
- California Earthquake Authority may reduce disaster benefits.
Russia-Ukraine War
- S&P has predicted that losses from this war could amount to almost $36B for the insurance industry.
- There has been an increase in cyber risks stemming from the conflict as well.
Uncertainty due to Brexit
- According to Aviva’s Risk Insight Report, business leaders have ranked Brexit as the fourth largest risk to insurance companies as its effects on the UK market place increased pressure on the US market to perform.
Social Factors impacting insurers in the US
- The insurance business is a complex, competitive industry that depends on many interconnected social factors, which need immediate attention
- Changes in consumer buying patterns and behaviors
Connected Millennials vs Gen Z
- Millennials are more likely to have auto and homeowners’ insurance than Gen Z
- Gen Z makes up around 30% of the global population, now outnumbering millennials
- Gen Z prefer buying insurance in person while millennials rely on mobile and internet
- Gen Z are digital natives who know the risks of over-sharing and are more selective in what they reveal about themselves, making them potentially more wary of sharing their data with insurers
- Millennials were early adapters to social media and shared everything
Insurance buying patterns for millennials
- There has been a sharp decline in home and auto ownership and an increase in participation in the sharing economy, changing the nature and attribution of risks
Diversity, inclusion, and equity (DEI)
- An emphasis on DEI has become a vital part of a brand’s outreach efforts.
Shifting consumer choices and needs
- Consumers are seeking products customized to their needs
- Looking for affordable policies due to less driving
Hybrid working model
- Consumers prefer pay-as-you-drive auto policies due to less frequent driving
- A greater adoption of hybrid working models is leading to work related injuries at home
Market competition and dynamics
- Changing dynamics have intensified price-based competition, driven market expansion into new geographies, and motivated insurers to develop new products
Technological factors impacting insurers in the US in 2022
- Rapid changes across the board with new technologies needing adoption
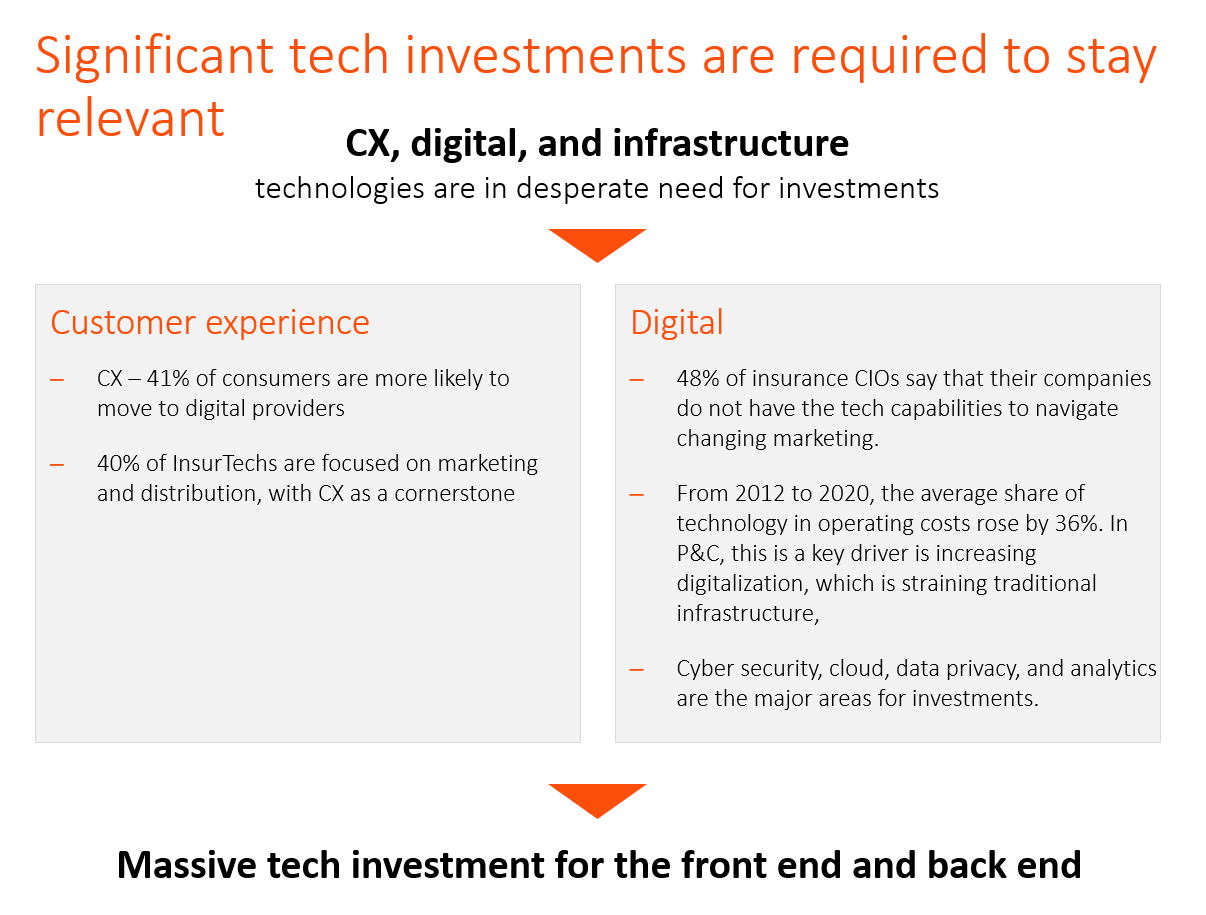
As insurers gear up to face the challenge from InsurTechs, a subsection growing at approximately 48%, they are trying to improve CX and digitizing their front end. However, they are facing an increasing need for investments back-end technology infrastructure to improve efficiency, mitigate threats, and cater to new demands. One pertinent example is most insurers are not equipped to handle the explosion of data generated by the estimation one trillion internet of things (IoT) devices expected to be in use by 2025.
Other technological trends
Outdated technology
- Outdated insurance technology infrastructure, such as legacy policy and underwriting systems, is obstructing growth and operating cost reduction.
Rapid data, digital, and new technologies
- There has been an increase in use of IoT devices, telematics, and automation.
- Insurers that leverage data analytics can make informed decisions and gain a competitive advantage.
- New technologies can help mitigate the major talent shortage facing the industry.
- The industry is seeing an increased need for streamlining core operational processes.
CX at the core
- Consumer trends are requiring the hyper-customization of insurance products using real time customer data.
- Customers expect faster claim settlements than ever before.
- Consumer engagement demands an ongoing customer focus, operational efficiency, process and people excellence, product and service innovation, agility, and organizational alignment
Automation driving efficiencies
- There is an increased need for faster policy and claims processing, driving a need for increased automation adoption
- Autonomous cars are being tested by Google, Volvo, Mercedes, Audi may lead to increased product liability for the manufacturers
Environmental factors impacting insurers in the US
- As CAT events increase in ferocity, reinsurers are covering themselves and a rapid response needed
- Increasing incidence and severity of CAT events
Economic impact of climate hazard
- The impact of climate hazards is expected to increase from about 2% of global GDP to more than 4% of global GDP by 2050
- Natural disasters have cost the United States more than $600B over the past five years
- Disaster events during 2020 caused $95 billion in costs to insurers. Considering inflation, this is the fourth-highest adjustment since 1980, and more than double the 41-year average of $45.7B.
Impact of a rapidly changing insured pool
- With increasing climate-related events, there is very high risk on a portfolio level. Pressure is now on carriers to price for true risk more precisely on a policy-by-policy level
- Reinsurers are moving quickly to exclude certain climate related risks out of contracts
Climate impact on investment portfolios
- A recent survey by BlackRock found that 95% of insurers expect climate change to affect how they build their investment portfolios
- Regulators are also taking action, as evidenced by New York’s recent guidance, setting the expectation that insurers analyze their climate risk as both underwriters and investors and report that risk to stakeholders
Impact of pollution
- Harvard research has found that people living in areas with poor air quality are more prone to fatal respiratory infections caused by viruses such as Covid-19
- By some estimates, half of the deaths caused by pollution in the Unites States are preventable
- Increasing plastic pollution is leading to higher health and marine pollution related liability claims
Legal factors impacting insurers in the US
- The regulatory challenges facing insurers will requiring be balancing the ever-growing list of high-priority areas for governing agencies
- More stringent regulations and privacy laws
Consumer privacy and data security laws
- Increased digitalization also creates an increased risk of data loss, which can lead to litigation in case of privacy breaches
- Insurers need to comply with data loss prevention acts like GDPR to ensure customer data is not compromised.
- Access to connected car data is a central part of the Right to Repair legislation now making its way through the courts
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is trying to understand more about the impacts of autonomous systems on real-world driving. A standing general order outlining reporting requirements the OEs and other companies must now meet has been published.
Increase in litigation against insurers
- Securities class action litigations are impact directors and officers.
- Cyber breaches, error and omissions, and defaulted mergers and acquisitions are also the behind increased litigation activities against insurers.
More regulation after COVID
- Auto premium refunds issued as part of pandemic relief are under regulatory scrutiny.
Russia-Ukraine War
- Assessing war-related claims must take legal factors into account, such as violating restrictions on entering a war-impacted country
- There have been increased restrictions on using services from Russia.
- Processing certain claims with war exclusions might lead to legal complications for insurers due to the use of different terminology. For example, in Russia, the war is being referred to as special military operation.
Anti-trust legislations to prevent monopolies
- Antitrust laws are statutes developed by governments may affect acquisition strategies
Employment and labor laws
- Insurers having operations in different countries must comply with the rules and regulations of the countries to avoid legal issues in regions that recently changed guidance or regulations around remote work
Author

Rup J. Goswami,
VP & Lead, P&C Growth Enablement Team
Rup is responsible for spearheading the growth of EXL’s Insurance P&C business as the lead of the P&C Growth Enablement Team. He has extensive experience managing various roles in Analytics, Consulting, Insurance, Financial Services, and Marketing.
Co-author

Raghav Jaggi,
Senior Vice President, Co-Head P&C Insurance and Insurance F&A Leader, EXL
Raghav is responsible for EXL’s Insurance Finance & Accounting Business and co-leads the Global P&C business. He has extensive experience in implementing and managing strategic client engagements across Target Operating Models, Digital, Data and Analytics.
Contributors

Aryashri Bhanshali,
Summer Intern, Insurance Management
Aryashri has been a student of Economics & Psychology from Wellesley College. She is currently working as a summer intern for research and insurance at EXL.

Kavita Chugh,
Manager, P&C Research & Growth Enablement Team
Kavita is a core member of the P&C Research and the Growth Enablement Team. She has over 13 years of experience in various roles spread across Research, Insurance, Healthcare, Operations Management, and Capability Development.

Akshat Khunnu,
Lead, P&C Research Team & Sr. Manager, P&C Growth Enablement Team
Akshat is responsible for leading the P&C Research team and is a core member of the P&C Growth Enablement Team. He has over six years of experience in multiple roles in Research, Insurance, E-commerce and Operations Management.
